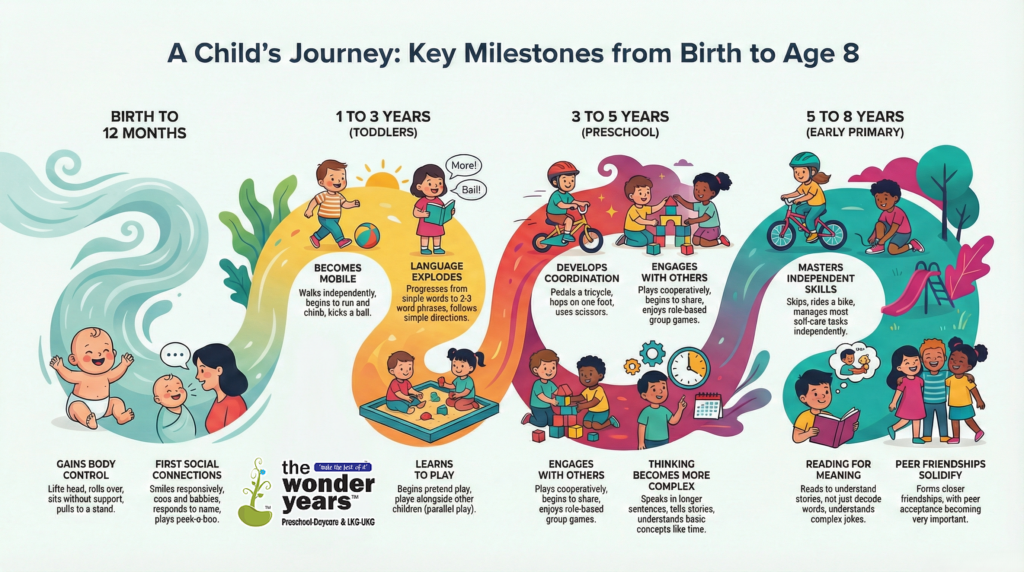
From birth to age eight, children usually progress through a predictable sequence of milestones across motor, language, cognitive, and social‑emotional domains, though the exact pace varies for each child. The ages below are approximate “most children can do by this age” guides, not strict cut‑offs.cdc
Birth to 12 months
- By 2–4 months: Lifts head and chest when on tummy, brings hands to mouth, follows faces and objects, smiles responsively, coos, and turns toward sounds.cdc
- By 6–12 months: Sits without support, rolls both ways, crawls or scoots, pulls to stand, responds to name, babbles (“ba‑ba”, “ma‑ma”), uses gestures (reaching, waving), and enjoys simple social games like peek‑a‑boo.chop
1 to 3 years (toddlers)
- Around 12–24 months: Walks independently, may start to run, points to show interest, uses several single words, follows simple one‑step commands, scribbles, and begins pretend play.medlineplus
- Around 2–3 years: Runs well, climbs, kicks a ball, uses 2–3 word phrases, names familiar objects, follows two‑step directions, begins to sort shapes and colors, and shows more independent and parallel play with other children.clevelandclinic
3 to 4 years (preschool)
- Motor and self‑help: Jumps with both feet, pedals a tricycle, walks up stairs alternating feet, puts on some clothing, and feeds self with minimal spilling.chop
- Language, thinking, social: Speaks in longer sentences, is mostly understood by familiar adults, knows some colors and basic counting, engages in make‑believe and cooperative play, and begins to share and take turns with guidance.nortonchildrens
4 to 5 years (foundation stage)
- Motor and coordination: Hops on one foot, catches a bounced ball, draws a person with several body parts, and uses scissors with supervision.medlineplus
- Cognitive and social‑emotional: Tells simple stories, understands basic time ideas (today/tomorrow), recognizes many letters or numbers, follows multi‑step directions, shows more self‑control, and plays rule‑based group games.clevelandclinic
5 to 8 years (early primary)
- By 5–6 years: Skips, rides a bike or similar, ties some clothing items with help, prints some letters and numbers, reads and writes simple words, and understands right/wrong rules more consistently.webmd
- By 7–8 years: Shows improved strength and coordination, reads for meaning rather than just decoding, understands more complex language and jokes, manages most self‑care independently, and forms closer peer friendships, with peer acceptance becoming very important.webmd
References:
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/21559-child-development
- https://www.cdc.gov/act-early/milestones/index.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/actearly/milestones/index.html
- https://www.hearingfirst.org/cfs-filesystemfile/__key/communityserver-components-sitefiles/CMS+Assets-Files-Downloads/hf_2D00_milestones_2D00_09062017.pdf
- https://www.webmd.com/parenting/child-8-milestones
- https://www.chop.edu/primary-care/developmental-milestones
- https://med.stanford.edu/content/dam/sm/pediatricsclerkship/documents/5-Developmental-Milestones-MedU.pdf
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002002.htm
- https://nortonchildrens.com/services/pediatrics/developmental-milestones-by-age/
- https://choc.org/ages-stages/
